
Quantization (signal processing) Wikipedia
Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping input values from a large set (often a continuous set) to output values in a (countable) smaller set, often with a finite number of elements. Rounding and truncation are typical examples of quantization processes.

Dave Swiston November 2014
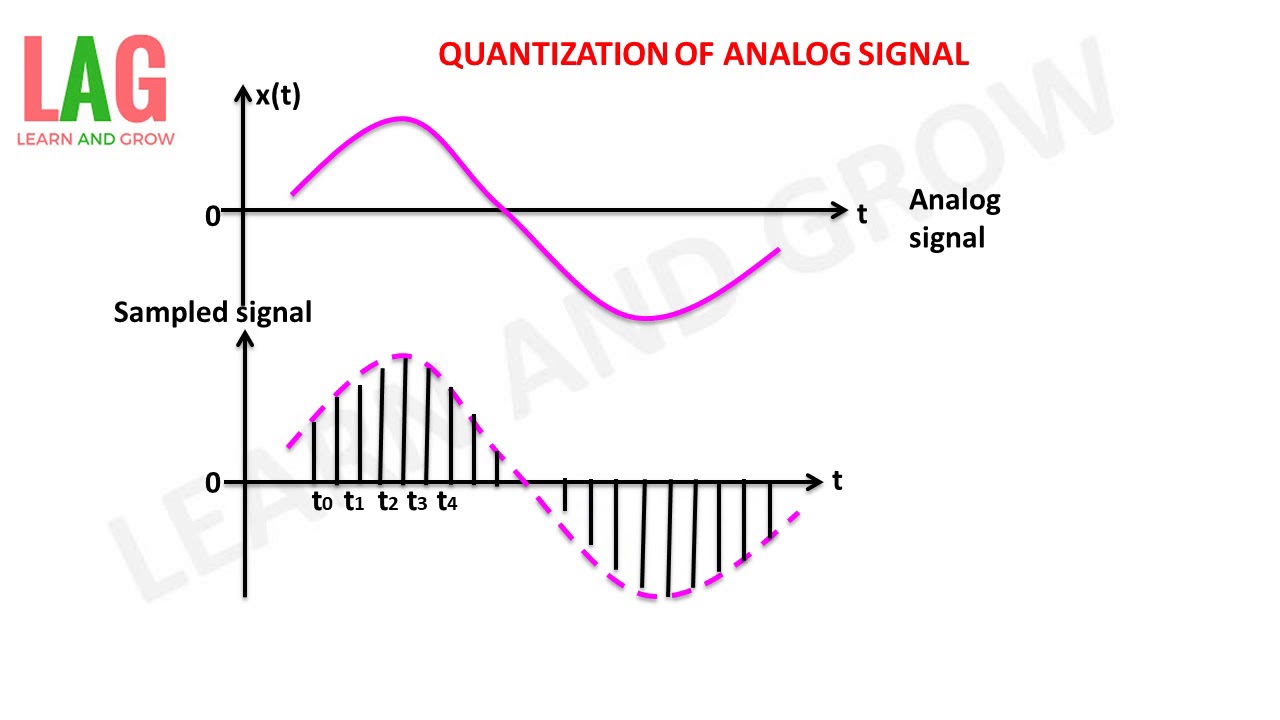
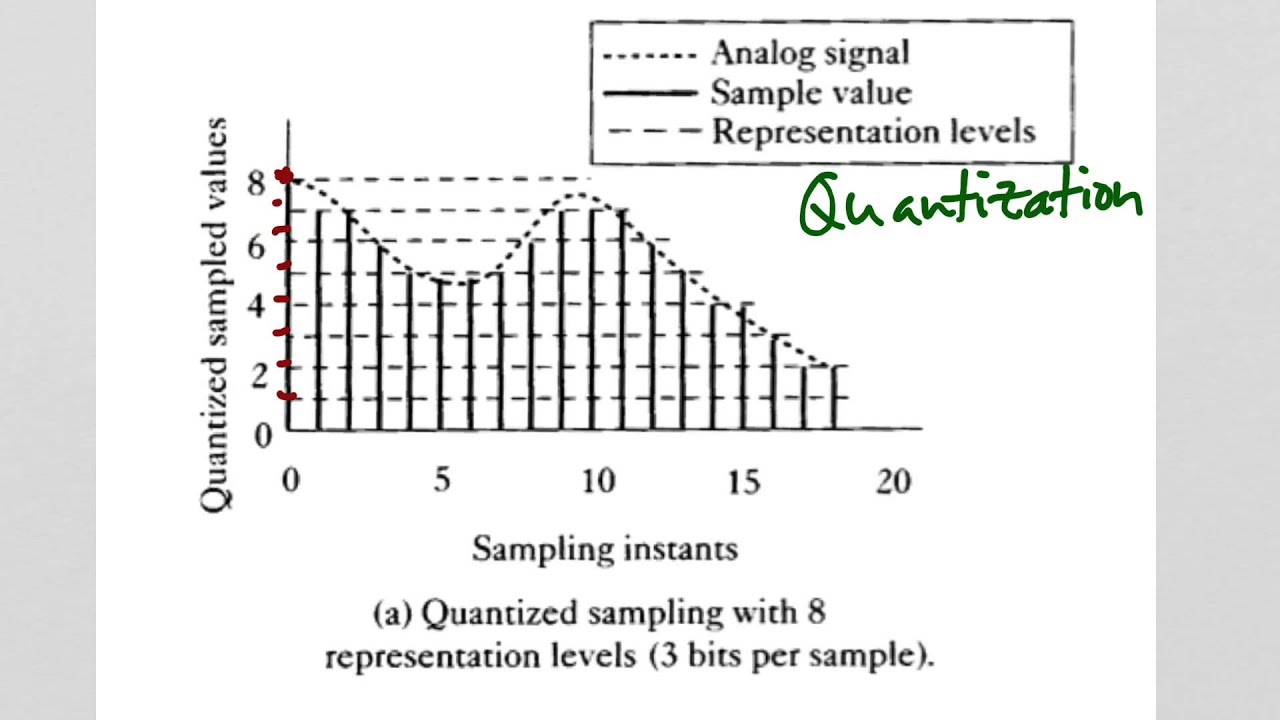
3.4 Quantisation of a signal When a continuous-time signal is sampled, the amplitude of each sampled point undergoes quantisation which means that it is forced to have only certain discrete values. The amplitude of each sample is represented by a digital binary code, and the word length of the code will be a fixed number of digital bits.

Quantization of neural signal with steps Download Scientific Diagram
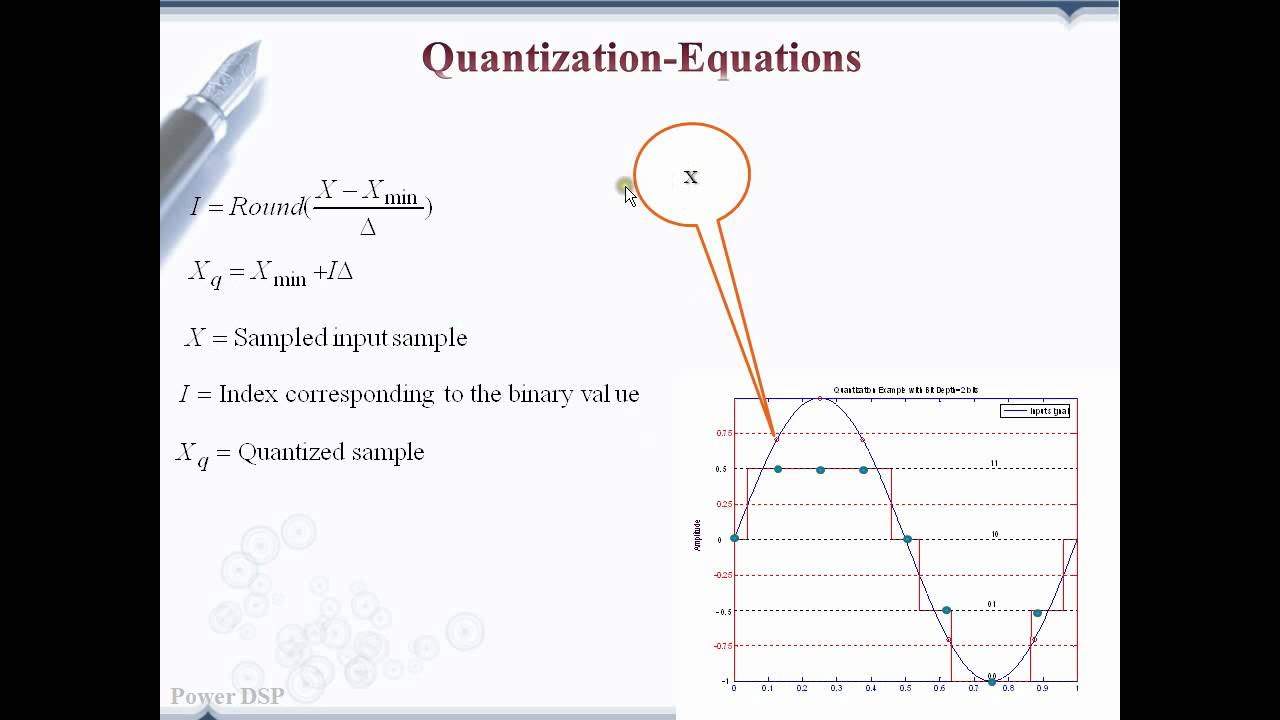
Quantization Basics. Given a real number x, we denote the quantized value of x as. ˆx = Q(x) = x + ǫ. where ǫ is the "quantization error". There are two main types of quantization: Truncation: just discard least significant bits. Rounding: choose closest value As an example, suppose we want to quantize 1. √2.
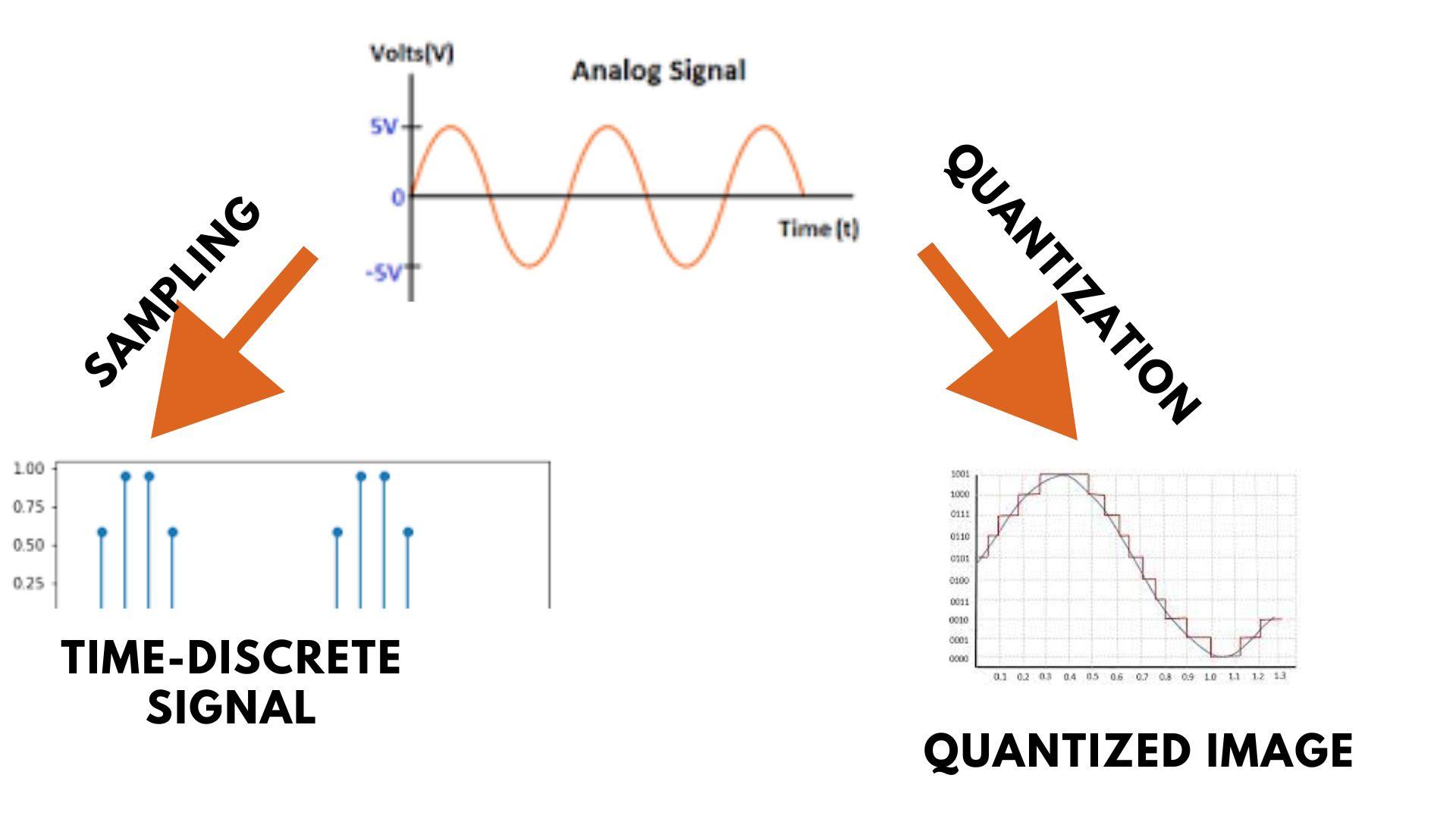
Image Sampling and Quantization Coding Ninjas
Quantization is the process of mapping continuous amplitude (analog) signal into discrete amplitude (digital) signal. The analog signal is quantized into countable & discrete levels known as quantization levels. Each of these levels represents a fixed input amplitude.

Sampling and Quantization of an Audio signal using MATLAB YouTube
Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping input values from a large set (often a continuous set) to output values in a (countable) smaller set, often with a finite number of elements. Rounding and truncation are typical examples of quantization processes. Quantization is involved to some degree in.

Signal Of Quantization Noise Ratio(Linear Quantization)(हिन्दी) YouTube
- Signal Processing Stack Exchange How we can quantize a sampled signal in MATLAB? Ask Question Asked 3 years, 10 months ago Modified 3 years, 10 months ago Viewed 7k times 0 I have a continuous time signal x(t) = sin(2πft) x ( t) = sin ( 2 π f t) where 0 ≤ t ≤ 3 0 ≤ t ≤ 3.
Quantization Of Analog Signal(हिन्दी) YouTube
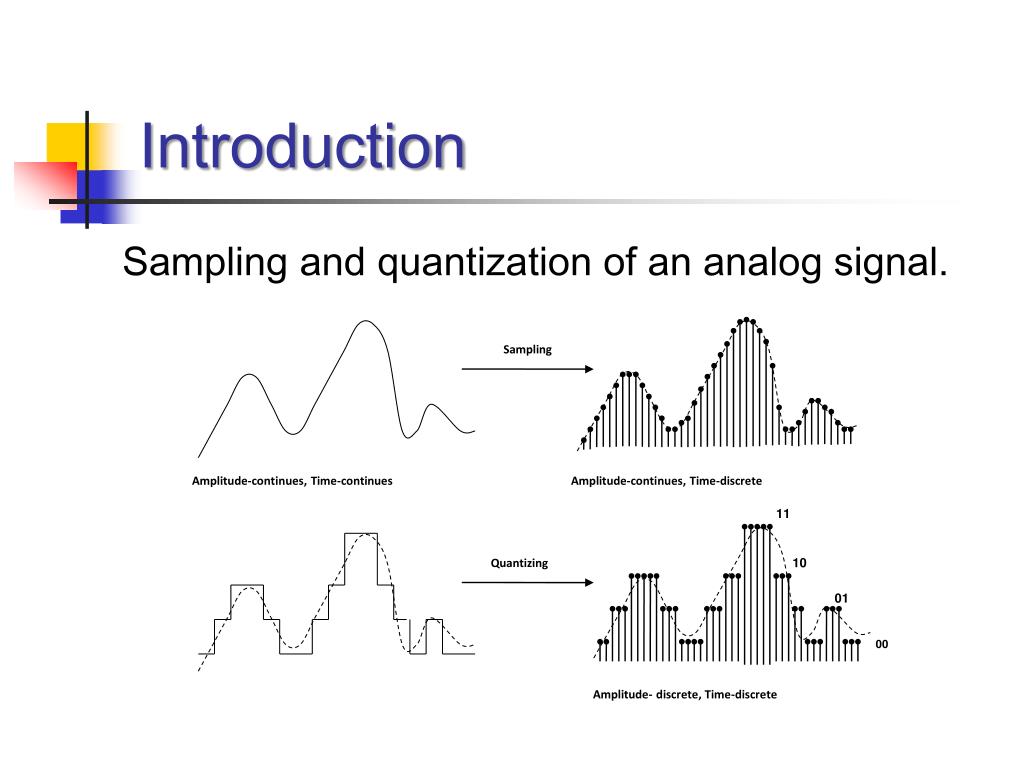
Chapter 2 Quantization. Basic operations for AD conversion of a continuous-time signal x(t) are the sampling and quantization of x(n) yielding the quantized sequence x Q (n) (see Fig. 2.1).Before discussing AD/DA conversion techniques and the choice of the sampling frequency f S = 1/T S in Chapter 3 we will introduce the quantization of the samples x(n) with finite number of bits.

C2S2_DigitalSignalQuantization
3.3 Quantisation. The sample values measured during sampling must be quantised to produce a digital representation of the analogue signal. That is, each value is approximated to its nearest quantisation level. Quantisation levels are pre-determined levels, like the rungs of a ladder, between the lowest possible sample value and the highest.

Quantization of a sine wave in an ideal quantizer, with quantum size =... Download Scientific
Quantization Marcel J. M Pelgrom Chapter First Online: 22 October 2021 3033 Accesses Abstract Quantization is the second main process in conversion. This chapter deals with the mathematical derivation and modeling of quantization in several resolution ranges.

Quantization and Companding Explained using MATLAB Audio Signal Analysis ADC 4.12 YouTube
The method of sampling chooses a few points on the analog signal and then these points are joined to round off the value to a near stabilized value. Such a process is called as Quantization. Quantizing an Analog Signal The analog-to-digital converters perform this type of function to create a series of digital values out of the given analog signal.
Quantization Part 3 Quantization understanding with equations YouTube
2.4.2. Defining precision and quantization. Precision, also known as bit depth, refers to how many bits are used to represent each sample in a digital signal. While we typically think of signals as taking on continuous real values, computers quantize these values to be drawn from a fixed, finite set of numbers.
PPT Survey of Quantization PowerPoint Presentation ID725091
The process of digitizing the domain is called sampling and the process of digitizing the range is called quantization. Most devices we encounter deal with both analog and digital signals. Digi-tal signals are particularly robust to noise, and extremely efficient and versatile means for processing digital signals have been developed.
Quantization "sampling" the amplitude of the speech signal YouTube
A digital signal is different from its continous counterpart in two primary ways: It is sampled at specific time steps. For example, sound is often sampled at 44.1 kHz (or once every 0.023 milliseconds). It is quantized at specific voltage levels.
quantization
Instructor: Dennis Freeman Description: Digital audio, images, video, and communication signals use quantization to create discrete representations of continuous phenomena. Efficient transmission and reconstruction uses techniques such as dithering, progressive refinement, and the JPEG encoding. Transcript Download video Download transcript

Original vs. quantized signal Download Scientific Diagram
Quantization refers to the transmission of an analog signal into a digital signal. It is the way of representing the sampled values of the amplitude by a finite set of levels. It is the process of converting a sample of continuous-amplitude signals into a discrete-time signal.

Quantization MATLAB & Simulink MathWorks United Kingdom
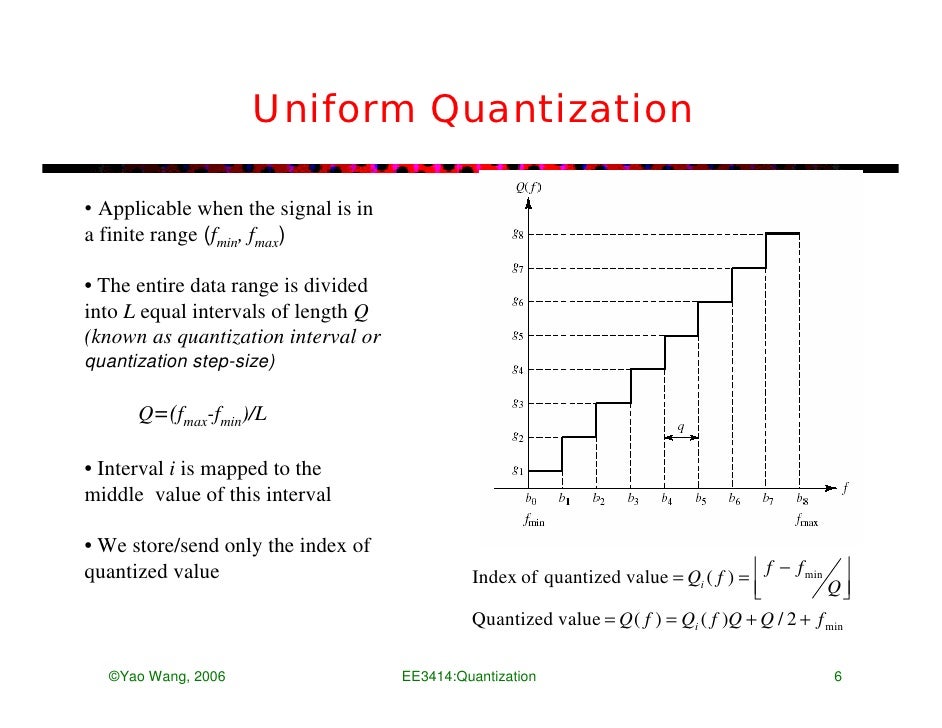
Quantization levels are the "centroid"of their region 2. Boundaries of the quantization regions are the midpoint of the quantization values Clearly 1 depends on 2 and vice versa. The two can be solved iteratively to obtain an optimal quantizer. Lloyd-Max algorithm: Start with arbitrary regions (e.g., uniform Δ)