PPT Connectionist Models of Language PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID626882
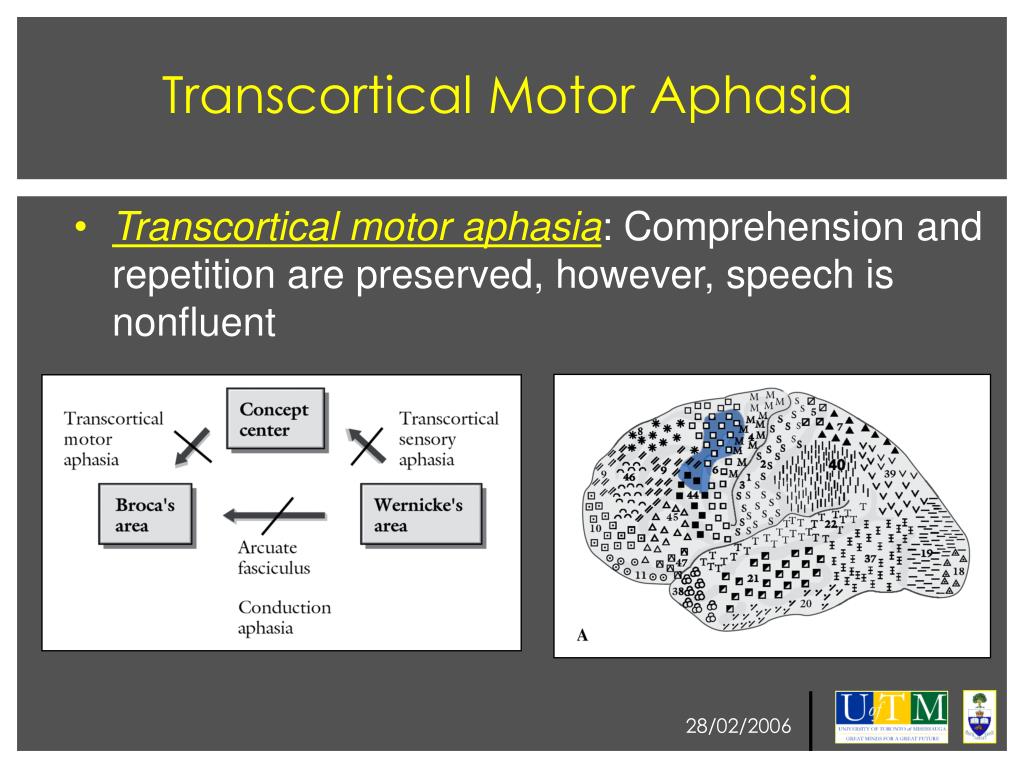
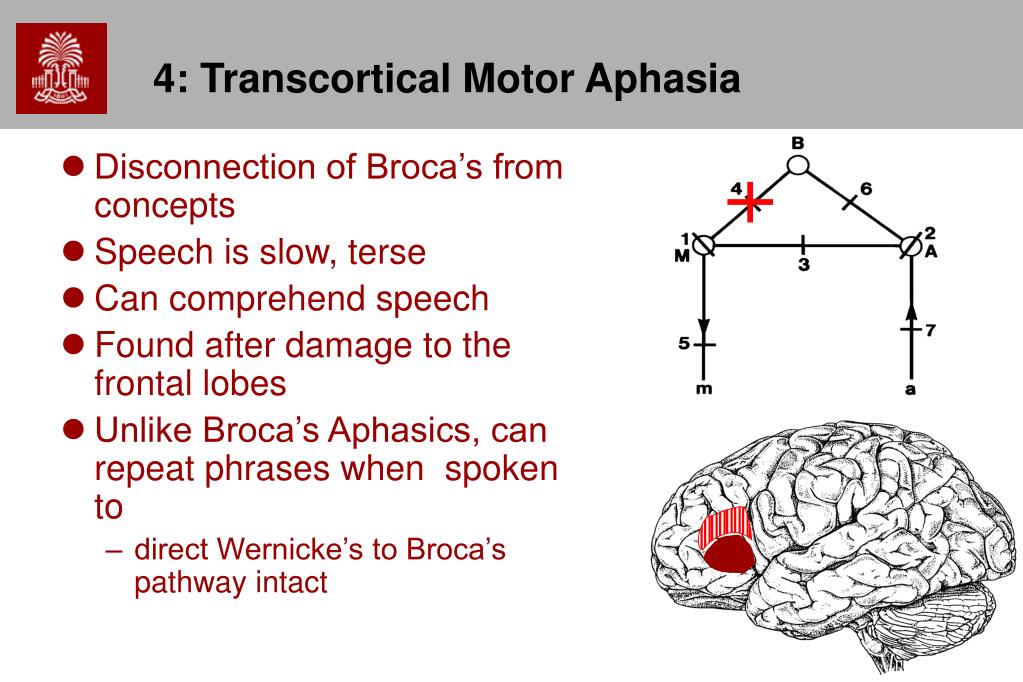
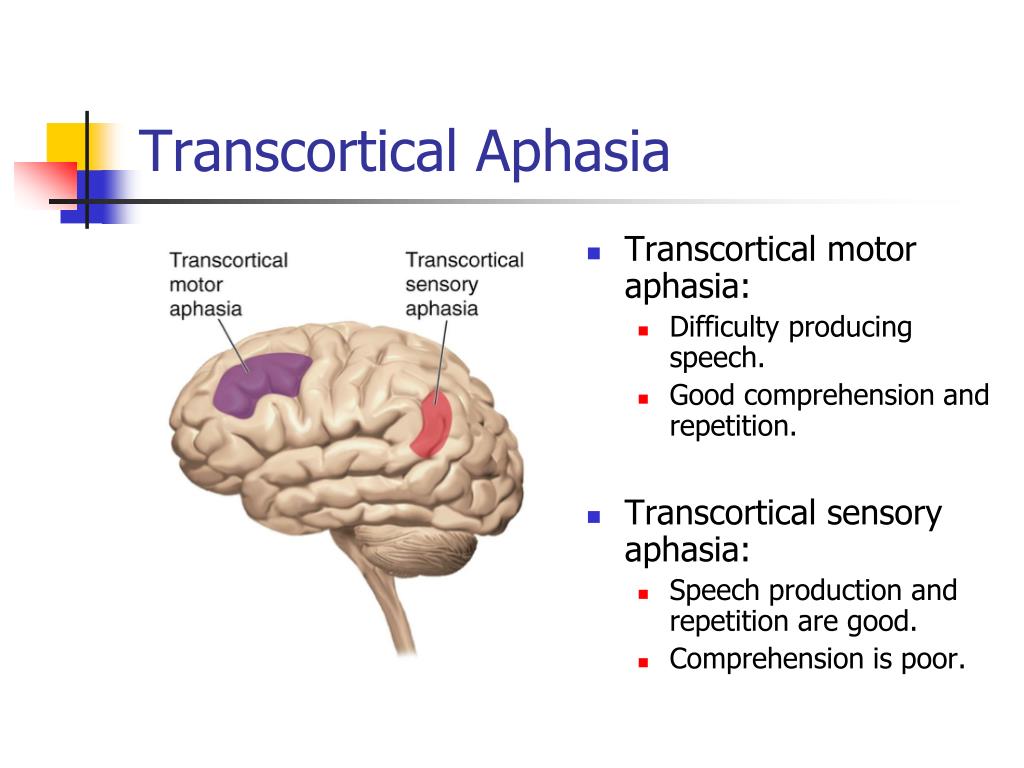
Transcortical motor aphasia is a subtype of nonfluent aphasia in which repetition is preserved relative to impaired verbal output. Expressive language is effortful and halting, with disrupted prosody, paraphasic errors, and perseveration. Confrontation naming may be intact.
Aphasia Types Flowchart
Support Group, and Group Interventions for aphasia, ABI, and specific acquired disorders;. Cognitive Disorders in Brain Injury and Disease, and Motor Speech Disorders. She has provided service in the adult rehabilitation arena for 37 years, in the roles of therapist, administrator, clinical supervisor, and teacher. Rebecca served on.
Different types of aphasias anatomoclinical correlations. Download Scientific Diagram
Transcortical motor aphasia with difficulty in initiating and organizing responses, but relatively preserved repetition. Mixed transcortical aphasia in which echolalia (repetition) is the only preserved language skill. Global aphasia characterized by severe impairment in speech and comprehension, and stereotypical utterances.
APHASIA, WHAT WE NEED TO KNOW ABOUT THIS DISORDER!!! — Steemit
Transcortical Motor Aphasia is a type of non-fluent aphasia. This means that speech is halting with a lot of starts and stops. People with TMA typically have good repetition skills, especially compared to spontaneous speech. For instance, a person with TMA might be able to repeat a long sentence.

PPT Aphasia PowerPoint Presentation ID421013
Transcortical motor aphasia resembles Broca's aphasia, but patients are able to repeat. The term transcortical aphasia was suggested by Wernicke in 1881 and Lichtheim in 1885. It was also termed anterior isolation syndrome by Benson and Geschwind.43 Verbal output is described as nonfluent and dysarthric, as in Broca's aphasia.
Brain And Aphasia
The defining symptoms of transcortical motor aphasia (TCMA) are nonfluent verbal output with relatively preserved repetition. Other symptoms, such as naming difficulties, agrammatic output, or even some paraphasias, may occur, but these are not cardinal symptoms defining TCMA and are not necessary for the diagnosis.

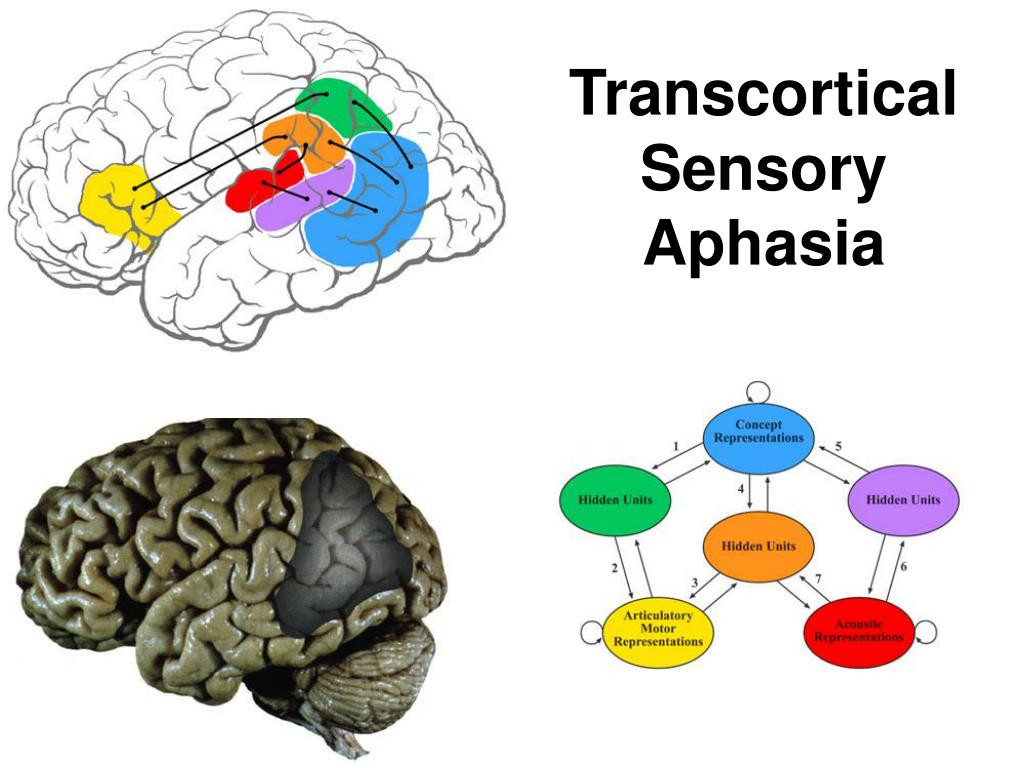
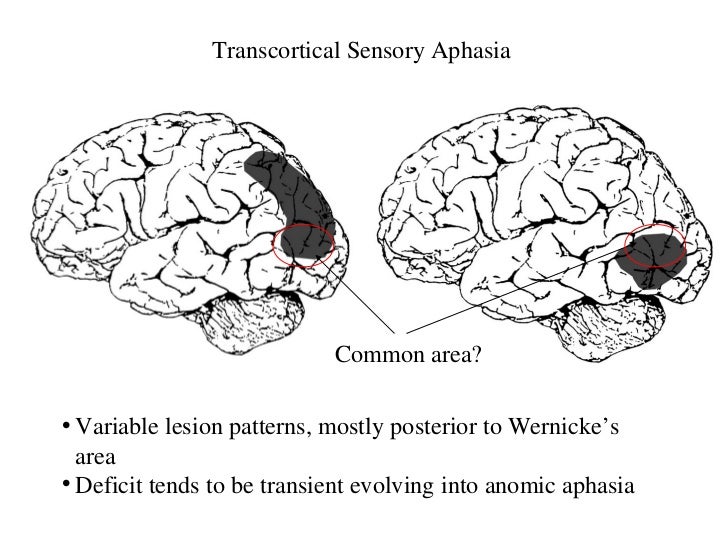
Figure 1 from Transcortical Sensory Aphasia after Left Frontal Lobe Infarction Loss of
Transcortical motor aphasia is a rare category of aphasia that can make it difficult to speak or understand others. The symptoms can very greatly between patients, which makes it critical to work alongside a speech therapist. Antidouleurs

Transcortical motor aphasia made easy clinical video aphasia broca’s aphasia stroke YouTube
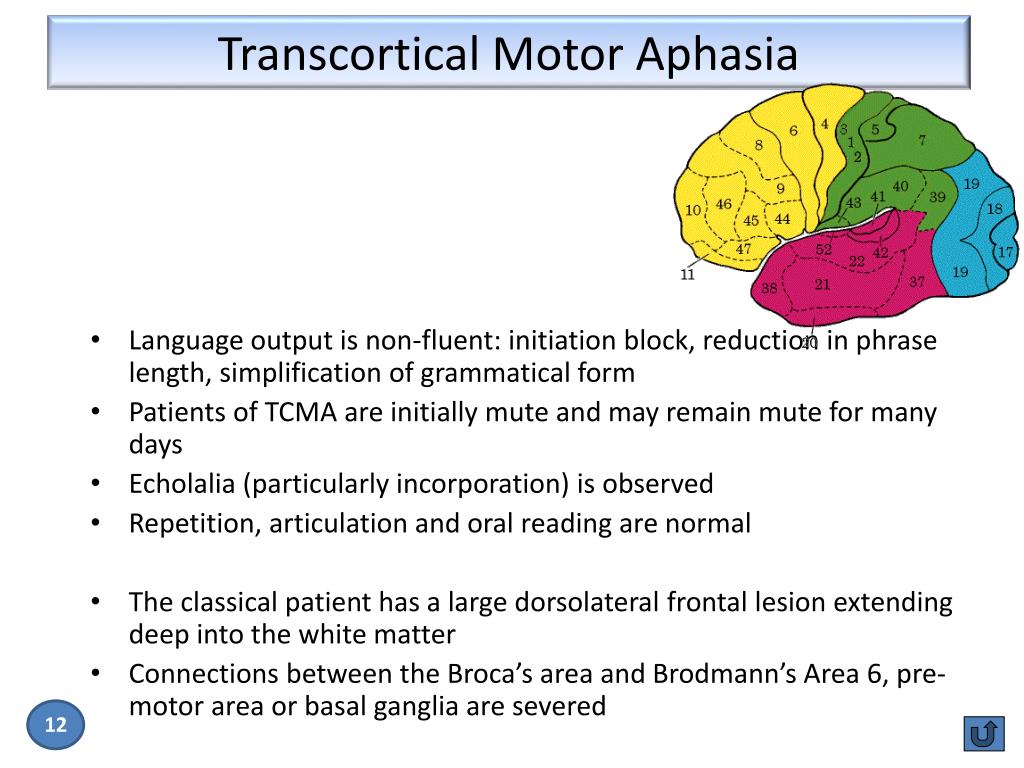
Analysis of language profiles and CT anatomy in transcortical motor aphasia (TCMA) suggests that the essential lesion is disruption of connections at sites between the supplementary motor area and the frontal perisylvian speech zone.

Figure 2 from Borderzone Strokes and Transcortical Aphasia Semantic Scholar
Transcortical motor aphasia ( TMoA ), also known as commissural dysphasia or white matter dysphasia, results from damage in the anterior superior frontal lobe of the language-dominant hemisphere. This damage is typically due to cerebrovascular accident (CVA).
PPT Language and Aphasias PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1195565
Transcortical motor aphasia is typically caused by a stroke located nearby Broca's area, just to the front of it. Transcortical Sensory Aphasia Stroke survivors with this rare type of aphasia cannot comprehend what others say but can speak fluently.
PPT Chapter 19 Higher mental functions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID389271
Transcortical Motor Aphasia, also known as commissural dysphasia or white matter dysphasia, results from damage to the language-dominant hemisphere in the anterior superior frontal lobe. Transcortical Motor Aphasia is classified as a non-fluent aphasia characterized by a significantly reduced speech output but good auditory comprehension.
PPT Chapter 13 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID73892
Aphasia is an impairment of comprehension or formulation of language caused by damage to the cortical center for language. It can be caused by many different brain diseases and disorders; however, cerebrovascular accident (CVA) is the most common reason for a person to develop aphasia.
PPT פרק א' קטגוריזציה מסורתית של סוגי אפזיה PowerPoint Presentation ID2131827
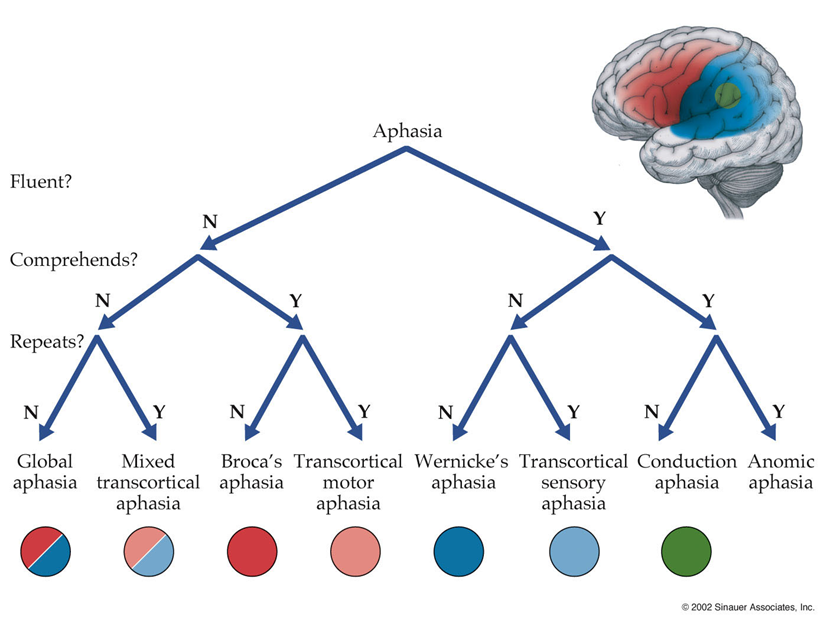
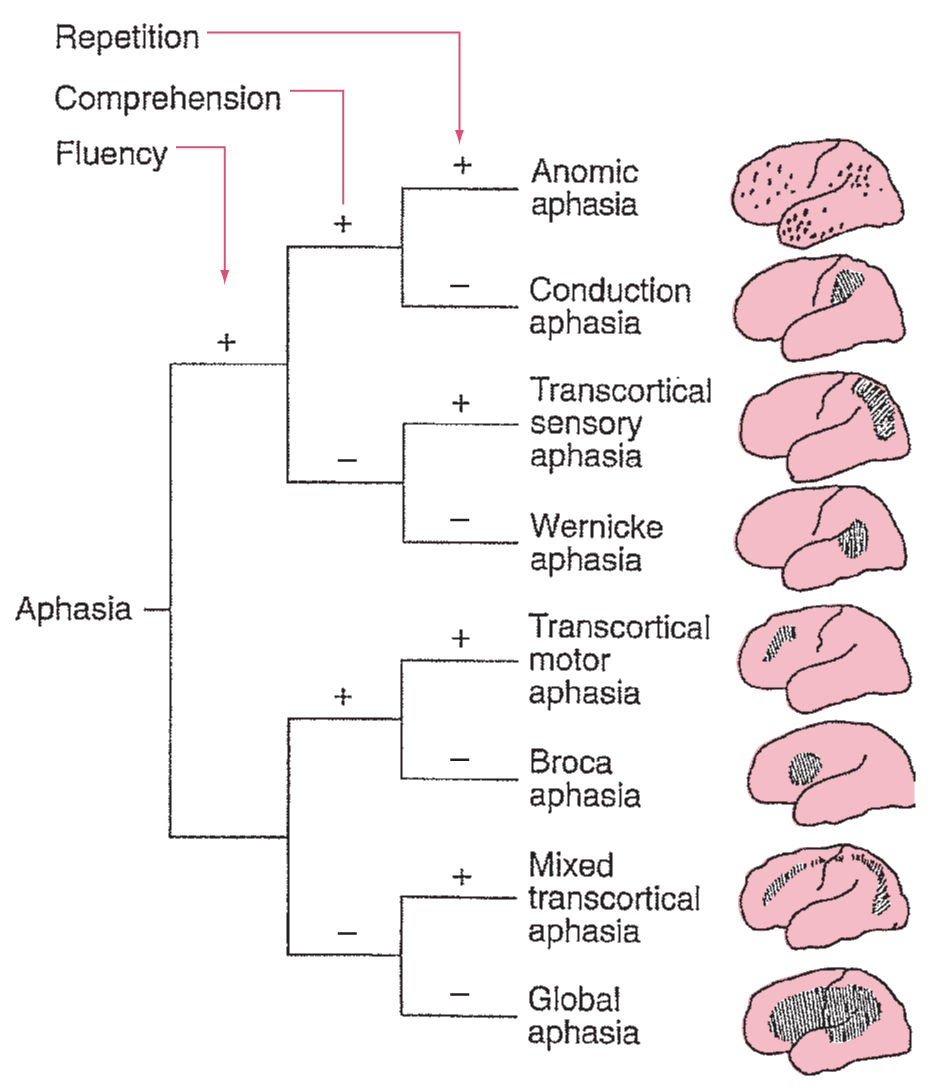
If an individual presents with non-fluent speech, they could potentially have Broca's, global, mixed transcortical, or transcortical motor aphasia. By contrast, if their speech was fluent, a clinician could surmise it to be Wernicke's, conduction, anomic, or sensory transcortical aphasia. During the diagnostic procedure, aphasic.
Approach to the Patient with Aphasia Neupsy Key
Transcortical Sensory Aphasia (TSA) has a lot in common with Wernicke's aphasia. People with TSA produce connected, flowing speech. However, that speech is likely to lack meaning due to word errors and invented words. TSA is less common than other types of aphasia, including the similar Wernicke's aphasia.

Pin en SpeechLanguage Pathologists (SLPs)
In transcortical motor aphasia, the language and comprehension are intact, whereas, in global aphasia, they are distorted. Transcortical mixed aphasia is also called isolation aphasia and it is equivalent to global aphasia. Comprehension of spoken language is severely disturbed in patients having this syndrome. It is common in occlusion of the.

PPT Chapter 13 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID73892
Aphasia is a condition that has a connection or an overlap with several other speech-related disorders and problems, such as dysarthria, dysphasia and apraxia. Aphasia: This is the overall term for a brain-connected problem with language abilities, including speaking or understanding other people speaking.