
human cell types Anatomy System Human Body Anatomy diagram and
A cell is the smallest living thing in the human organism, and all living structures in the human body are made of cells. There are hundreds of different types of cells in the human body, which vary in shape (e.g. round, flat, long and thin, short and thick) and size (e.g. small granule cells of the cerebellum in the brain (4 micrometers), up to the huge oocytes (eggs) produced in the female.

Human cell anatomy and organels diagram
The 46 chromosomes of a human cell are organized into 23 pairs, and the two members of each pair are said to be homologues of one another (with the slight exception of the X and Y chromosomes; see below). Human sperm and eggs, which have only one homologous chromosome from each pair, are said to be haploid (1n). When a sperm and egg fuse, their.

Explain the nucleus of a cell with a neat labeled diagram Science
Interactive guide to stem cells and cell biology with 3D models and real microscopy data of GFP labeled hiPSCs.

human cell diagram with labels
How many cells are in the human body.. Now you see it in this diagram right over here. This is not a common feature to all cells but the only reason why I'm mentioning it in this video is officially, the cytoplasm does not include the stuff inside the nucleus. In a eukaryotic cell, that is called the nucleoplasm but we'll talk more about.
Cells Haleo
Cells of humans typically have a mass 400,000 times larger than the mass of a single mycoplasma bacterium, but even human cells are only about 20 μm across. It would require a sheet of about 10,000 human cells to cover the head of a pin, and each human organism is composed of more than 30,000,000,000,000 cells.

Update 57+ human cell drawing latest nhadathoangha.vn
?µ 'šÔ "0nâc çûÏL? .§×Hg$Í \EQK‹)yI¢ ÛqmñÔOü] '°A€ Jb ûß›Zï†ÿ{Y[¹|$eÊÖRÎ$±óçÞûÞêu7Zj€d rJ w¶ŠàŸ ÇTqÖÜ÷Ú Ñ.

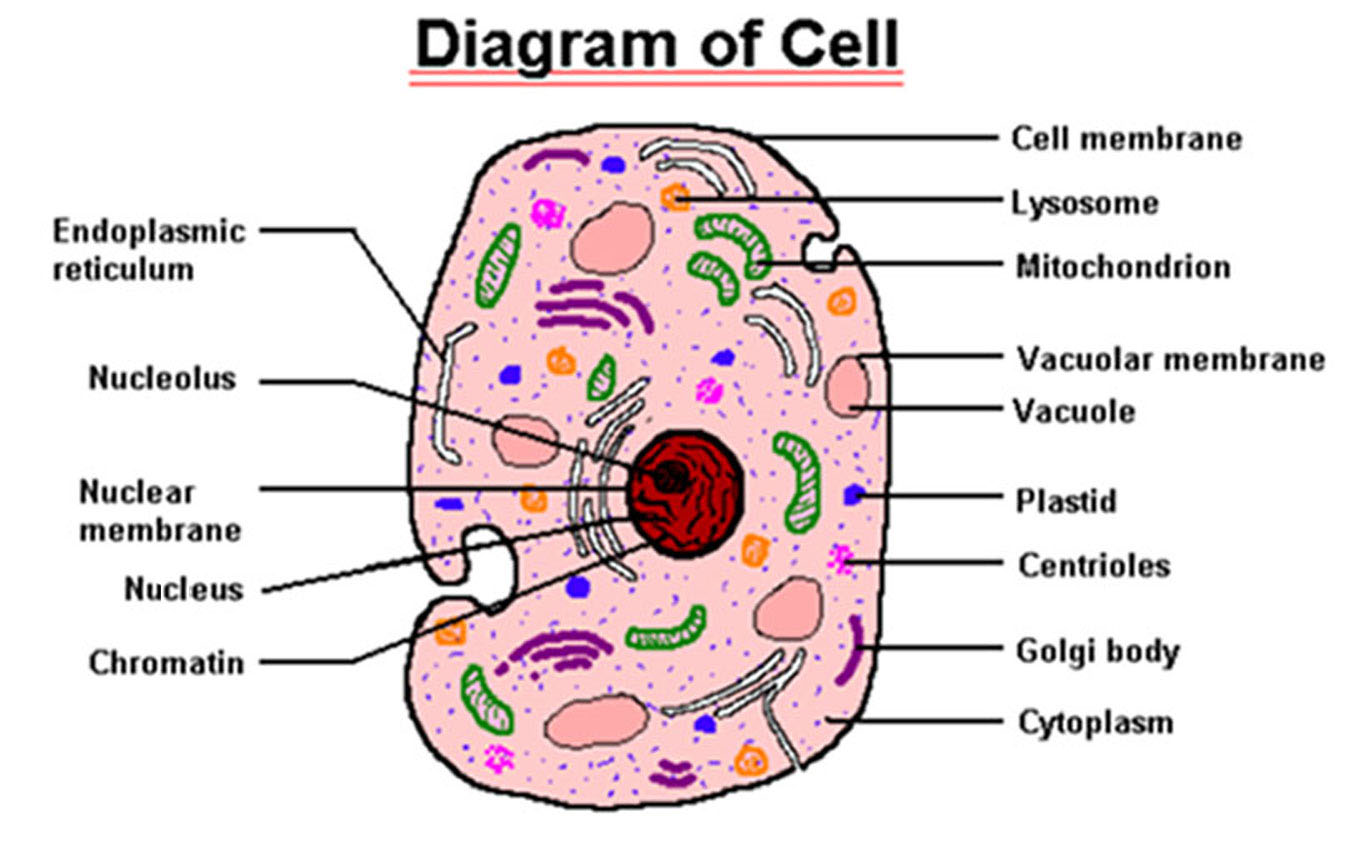
Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions
The diagram shows five levels of organization in a multicellular organism. The most basic unit is the cell; groups of similar cells form tissues; groups of different tissues make up organs; groups of organs form organ systems; cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems combine to form a multicellular organism.. The human body consists of.
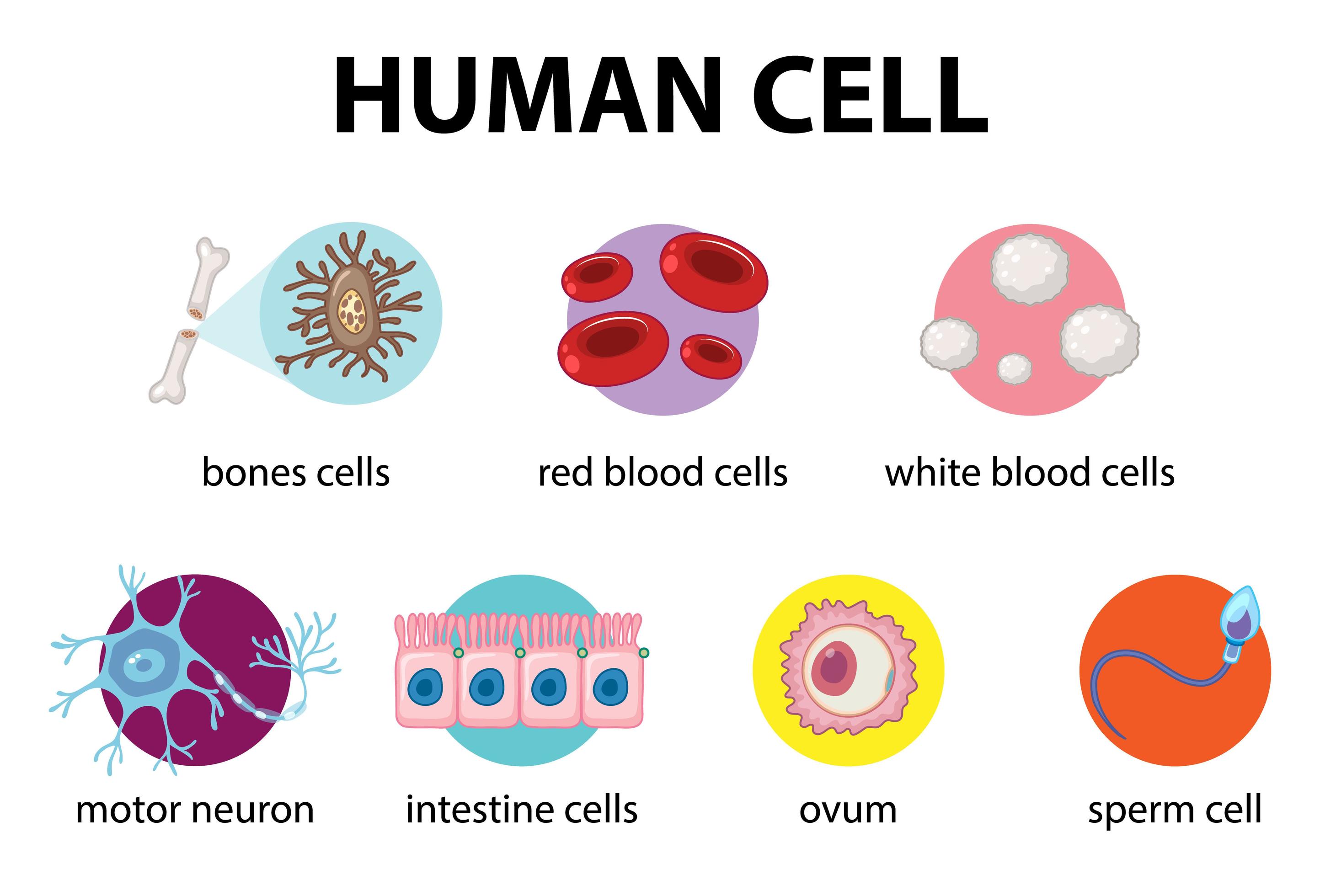
Diagram of human cell for education 1762228 Vector Art at Vecteezy
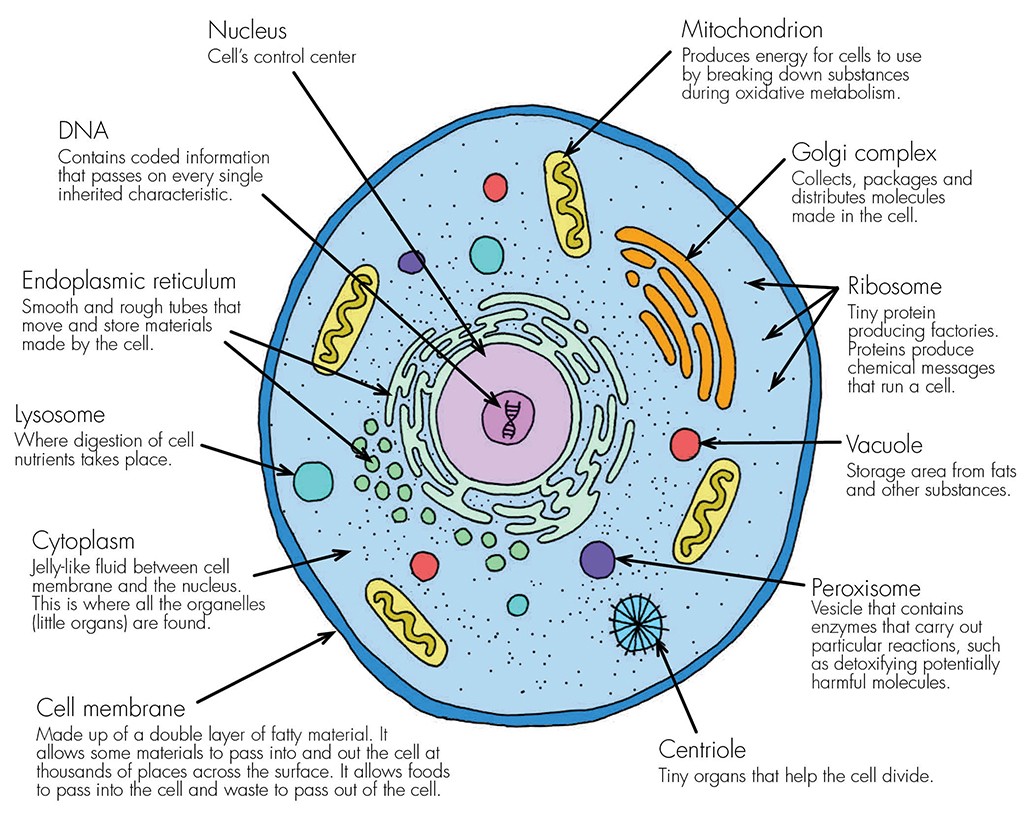
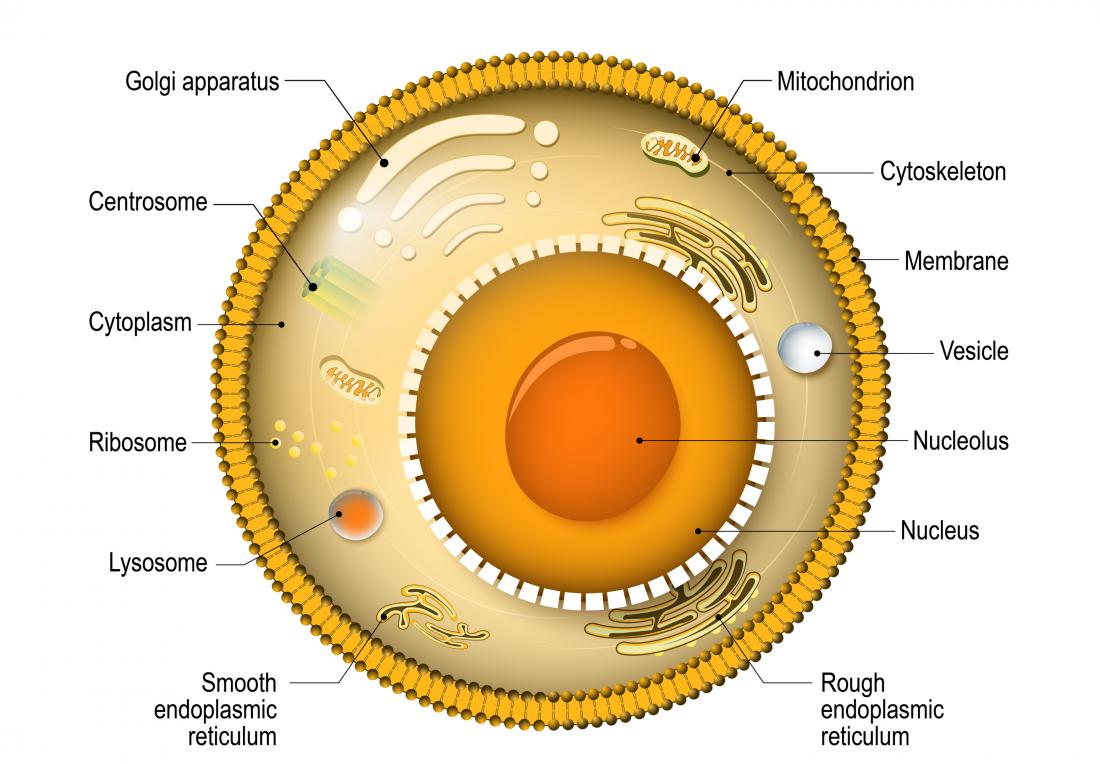
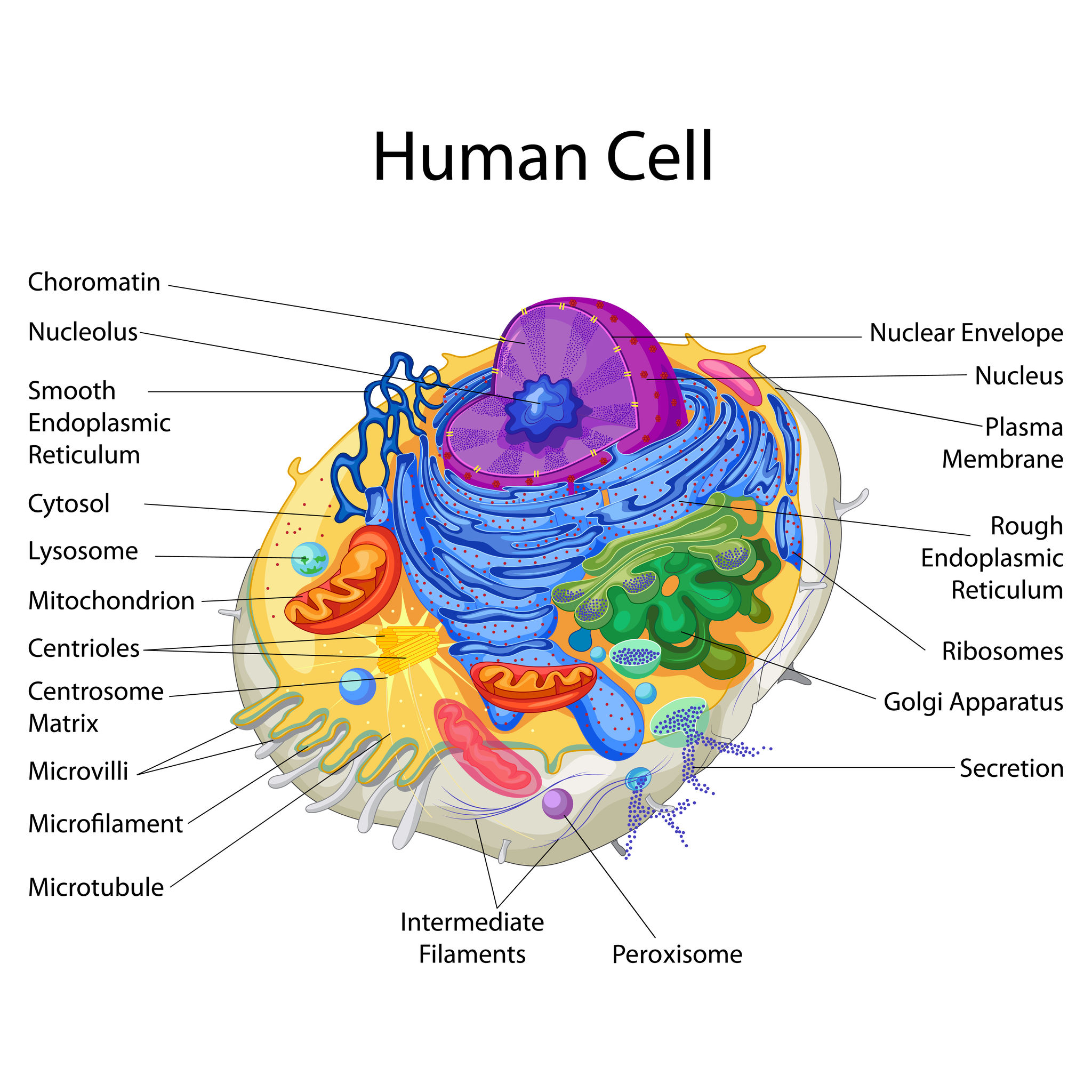
A diagram representing the cell as a factory. The cell membrane is represented as the "factory walls." The nucleus of a cell is represented as the "blueprint room.". Below is a table of the organelles found in the basic human cell, which we'll be using as our template for this discussion. Organelle Function Factory part; Nucleus: DNA Storage:

Pin by james paterson on A (growing) list of people, places and things
Human Cell - Properties, Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure. By Thulasi Ram. The cell is the basic unit of any living organ and it is the organ that replicate on its own determining growth. The cell does not need any other triggering element for its multiplication since it is self contained. Cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in the.
The cell Types, functions, and organelles
As human skin needs water and food to keep the cells in shape, the plant cells need sunlight to make their energy and sugar. Human cells do not make energy, plant cells do. In fact, humans are animals that eat energy and plants are a good food because they have energy stored. Also, plants don't need more than the sun and water to get energy.
Education Chart of Biology for Human Cell Diagram Best Acupuncture llc
The Human Cell Atlas is likely to impact almost every aspect of biology and medicine, leading to a richer understanding of life's most fundamental units and principles.Some examples of what a cell atlas is helping scientists and physicians do: Provide a reference map for comparing related cells and identifying new cell types, states (behaviors), and how cells transition among them.

Human Cell Diagram Cell diagram, Human cell diagram, Plant and animal
An Introduction to the Human Body. 1.0 Introduction. 1.1 How Structure Determines Function. 1.2 Structural Organization of the Human Body. 1.3 Homeostasis. 1.4 Anatomical Terminology.. The cell membrane is an extremely pliable structure composed primarily of two layers of phospholipids (a "bilayer"). Cholesterol and various proteins are.

The Human Cell Atlas An international effort
Cell Structure. Ideas about cell structure have changed considerably over the years. Early biologists saw cells as simple membranous sacs containing fluid and a few floating particles. Today's biologists know that cells are infinitely more complex than this. There are many different types, sizes, and shapes of cells in the body.
Education 645 High School Biology
Diagram 2: The human cell membrane. Image Source: www.curezone.org. Cytoplasm/Protoplasm. It is the fluid inside the cells, which allow a number of cell organs to float inside the cell. It contains a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane. It consists of molecules, enzymes, fatty acids, sugar, and amino acids. (3)

Cell Structure And Function Cells The Basic Units Of Life Siyavula
Detailed diagram of lipid bilayer of cell membrane. The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is a selectively permeable biological membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell.. Human cancer cells, specifically HeLa cells, with DNA stained blue.

Pics Photos Human Cell Structure Diagram
Cells. The most basic parts of the human machine are cells—an amazing 100 trillion of them by the time the average person reaches adulthood! Cells are the basic units of structure and function in the human body, as they are in all living things. Each cell carries out basic life processes that allow the body to survive.